Hello friends, in this article, I will show you how to scan an application developed with .Net Framework 4.8 technology using Fortify.
Visual Studio 2019 IDE
For IDE scanning, we enter the relevant project folder and open the application from the solution file.

Then we start the scan by selecting Extension -> Fortify -> Analyze solution.
It will be sufficient to select Analyze solution to scan an application at solution level or Analyze Project to scan at project level.

When the scan starts, the screen will be as follows. Here we wait for the scan to finish without doing anything. We can check whether the scan gives an error by looking at the logs falling to the Output during the scan.
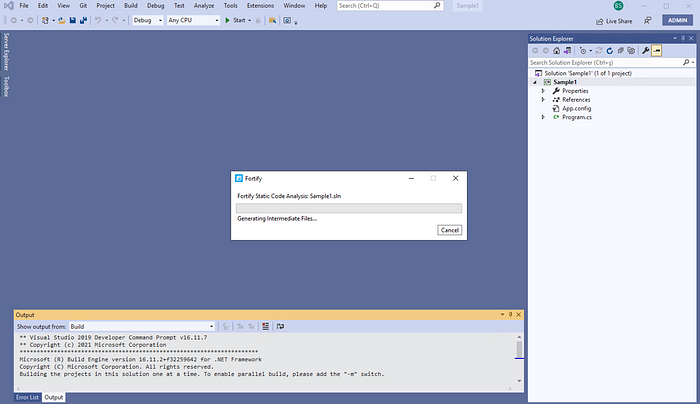
When the scan is finished, the Analysis Results screen will be opened on Fortify Visual Studio, as in the picture below, and the detected vulnerabilities will be displayed.

Scan Wizard
When Scan Wizard is run, the screen will be as below.

The first thing we need to do is to select the folder where the project to be scanned is located.
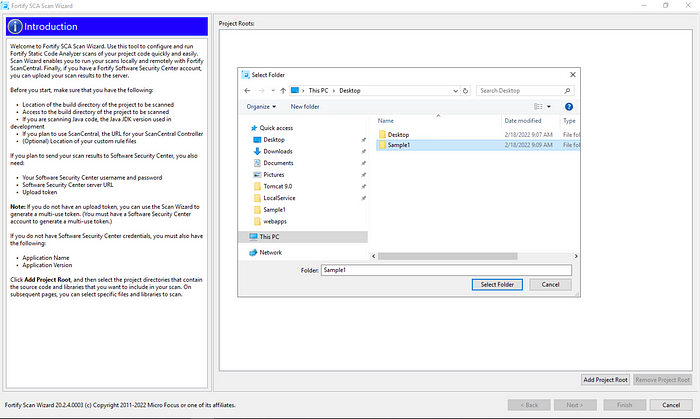
After making the selection, press next and we will see the screen as below. On the right side of the screen, we see that C# and XML sections are selected, and MSBuild and Visual Studio sections can be selected at the bottom.
At this stage, Scan Wizard examines the files in the folder we provide, detects the language of the application to be scanned, and offers us an option for this. MSBuild and Visual Studio options are presented here.
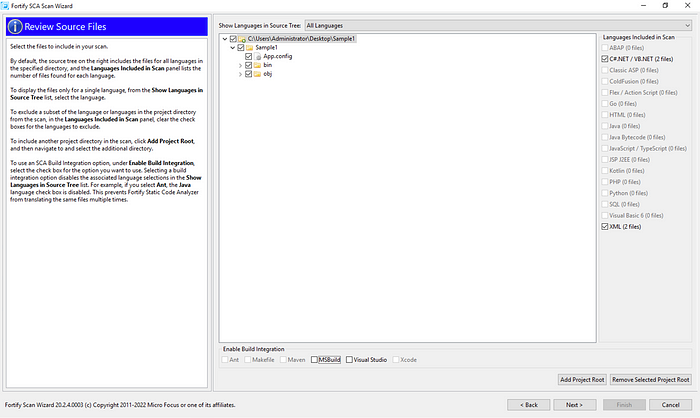
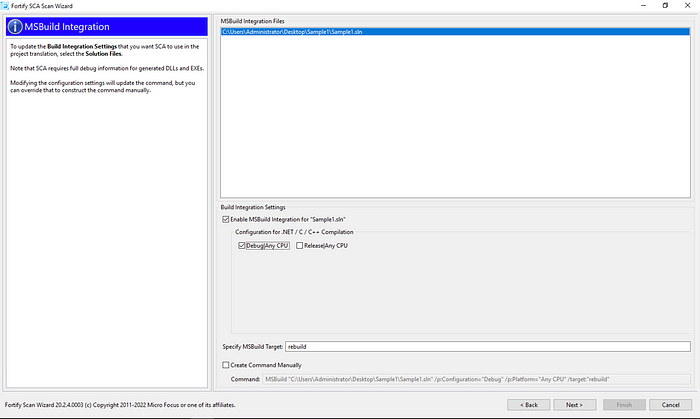
We mark MSBuild and click next to move on to the next step.

Fortify will use MSBuild to scan. Below shows us that the relevant project has detected the solution file. Make sure that there is the correct solution file here. In addition, make sure that the “Build Integration Settings” section is as follows. After the controls, we move on to the next step.
Scan Wizard generates .bat for Windows and .sh file for MacOS/Linux while scanning. Since we will perform the scanning process on Windows, we want the .bat file to be created and we can position this batch file anywhere we want. Here I set the bat file to be included in the relevant project.
- Quick scan : Just scan for High and Critical vulnerabilities. (It can be selected to save time in large projects, but other level vulnerabilities will not be obtained.)
- Upload Scan to SSC : Uploading the FPR file created after scanning to SSC.
- ScanCentral scan : Scanning of the application is performed by ScanCentral connected to SSC.
- Include Custom Rule : It is the inclusion of personal rules created in the scan.
After we’re done here, let’s click next and move on to the next page.

In this step, Scan Wizard shows us the bat file it will create as a summary. Here, if you want, you can come back and check or make changes on it by clicking back. I click finish button and finish the process.

When I come to the relevant project and check it, we can see the bat extension scan file created by Scan Wizard. Here I come to the project directory via cmd.exe and make the bat file work.
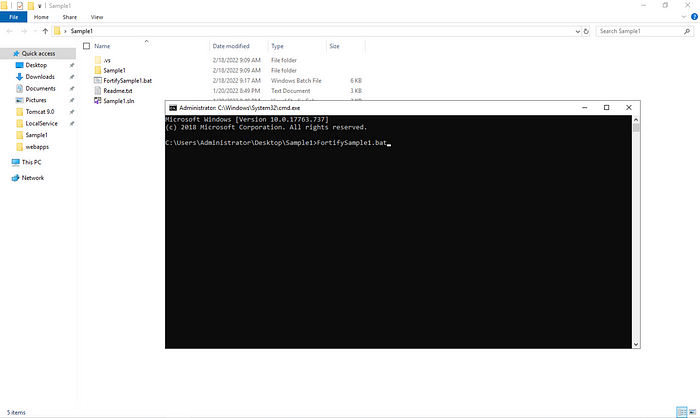
If there is no problem during scanning, the screen will be as follows. After this step, you can open FPR and view the vulnerabilities.

Terminal
Scan with MSBuild
Optionally, you can scan the source codes you want to be scanned by calling Fortify sourceanaylzer via CMD/Terminal.
I open a cmd.exe that looks at the location of the project to be scanned.

In this step, we will need to enter a command like the one below.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id -cleanThe explanations of the above command are as follows.
- sourceanalyzer.exe : The exe that Fortify uses to scan the source code.
- -b : You can think of it as a session in a web application. Here Fortify will use the name we give when it wants to keep the data it obtained for the project to be scanned in a field and access this field.
- -clean : If there was a scan using this name before, we empty it by saying -clean here. We have never used this name before, but it is recommended to be used in this way in best practices.

After the clean process, Translation (It is the process of making the codes to be compiled in a way that fortify can understand.) needs to be done. For this we enter the following command.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id msbuild /t:rebuild project.slnThe explanations of the above commands are as follows.
- “msbuild /t:rebuild “: Fortify will use msbuild as a scanning method and compile the relevant project and then translate the output it obtains. MSBuild will be used in the in-between conversion.
- “project.sln” : It is the part where the solution file to be scanned is named.
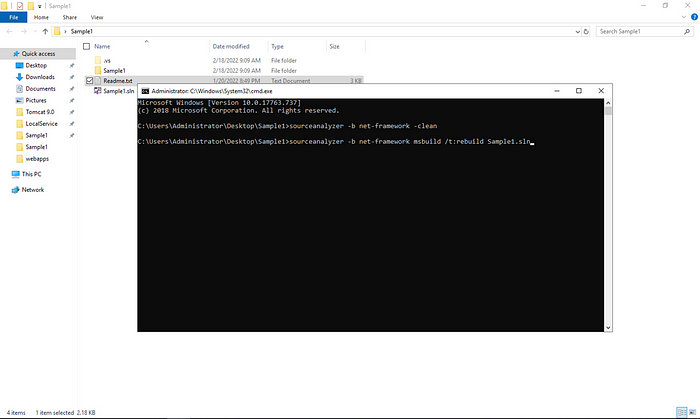
The post-processing screen using MSBuild will be as follows. What we need to pay attention to here is whether there is a build success text.
If we see the build success fail, it means that the related project encountered an error while scanning with MSBuild. Here it is necessary to fix that error. Since we see success, we can continue.

This step is the part where the codes compiled with MSBuild will be scanned and the outputs will be produced. For this, you will need to enter a command like the following.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id -scan -f output.fprThe explanations of the above commands are as follows.
- -scan : By giving this parameter, we ensure that the codes that are compiled and made understandable by fortify are scanned..
- -f : An FPR file will be generated for the vulnerabilities detected after the scan. Here we specify the name of the FPR file to be produced.
The vulnerabilities will be written on cmd.exe in scans where we forget the “f “ parameter.

When the scanning operation is finished, the screen will be as follows. When we look at the folder where the application is located, you can see that the FPR file has been created.

Scan with Devenv
Scanning steps with Devnev are mostly the same as with MSBuild. In order not to prolong the article, I will not explain the parameters I explained in MSBuild here again. You can check it above if you wish.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id -clean
Since it uses devenv here, it is necessary to enter a command like the one below.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id devenv project.sln /REBUILD Debug- “devenv /REBUILD Debug “Fortify will use devenv as a scanning method and compile the relevant project and then translate the output it obtains. Devenv will be used in the translation process in between.
- “project.sln” : It is the part where the name of the solution file to be scanned is given.

This step is the part where the codes compiled with Devenv will be scanned and the outputs will be produced. For this, you will need to enter a command like the following.
sourceanalyzer.exe -b build-id -scan -f output.fpr
When the scanning operation is finished, the screen will be as follows. When you look at the scanned folder, you can see that the FPR file has been created.

Thank you for reading my article.
